Resilience: The Cornerstone of Lasting Mental Well-Being

Photo by Jametlene Reskp on Unsplash
Understanding Resilience and Its Impact on Mental Well-Being
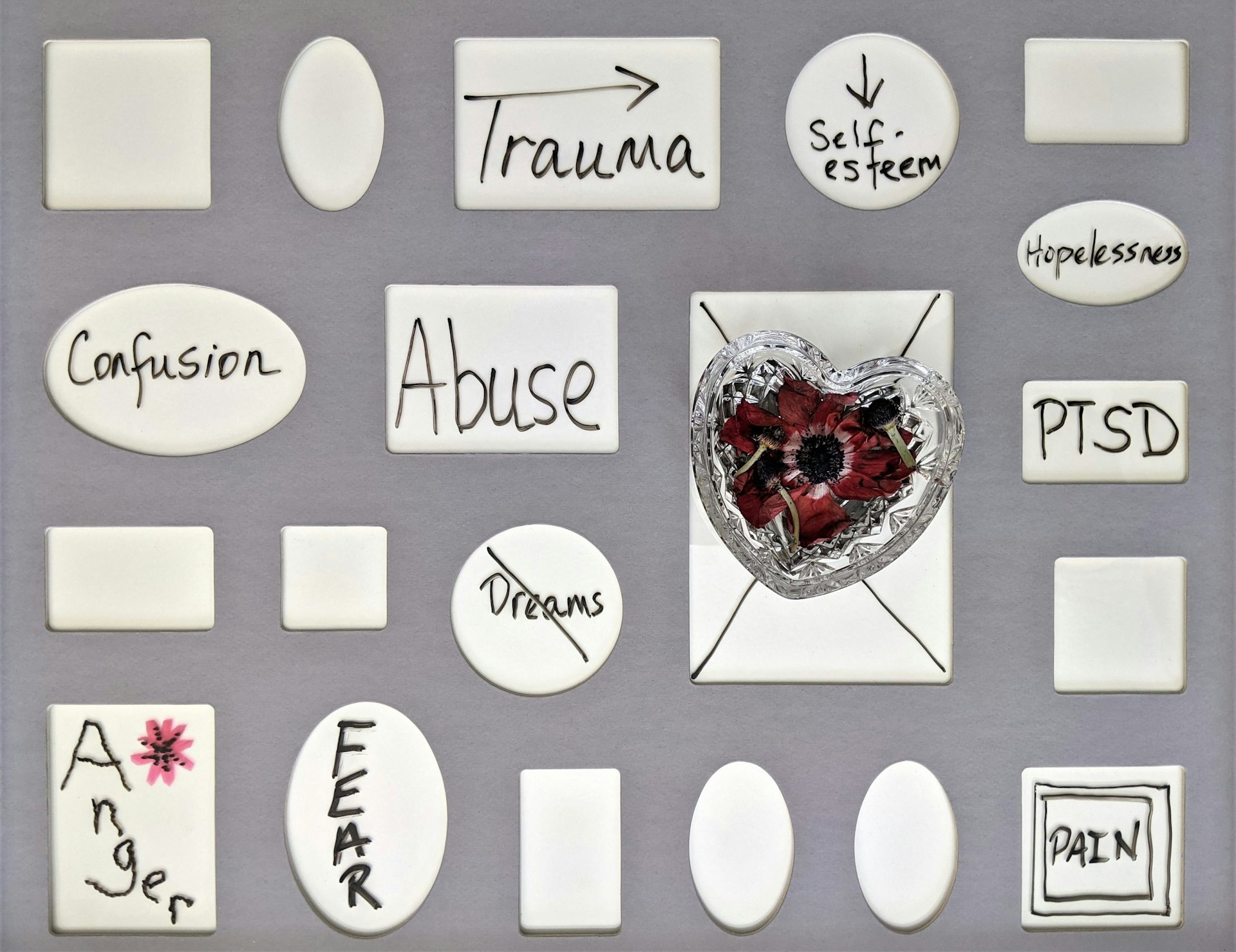
Resilience refers to an individual’s ability to adapt and recover from adversity, trauma, stress, or significant life changes. Far from being an innate trait, resilience is a dynamic process that can be learned and strengthened throughout life [2] . The World Health Organization emphasizes that mental health is not merely the absence of disease, but a state of well-being where individuals realize their abilities, cope with normal life stresses, and contribute to their communities [3] . Resilience is essential in achieving this positive dimension of mental health, serving as a buffer against the psychological impact of adversity.
The Protective Role of Resilience Against Mental Health Challenges
Extensive research demonstrates that high resilience is correlated with lower rates of depression and anxiety, greater satisfaction with life, and even increased longevity [2] . For individuals facing major life changes, such as bereavement, illness, or job loss, resilience provides the psychological tools needed to adjust, maintain stability, and recover. Studies show that resilient individuals are better equipped to manage chronic stress and its physical consequences, including high blood pressure, weakened immunity, insomnia, and digestive problems [2] . In clinical populations, such as those with bipolar disorder or posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), higher resilience is associated with fewer depressive episodes, reduced impulsivity, and lower PTSD symptoms [1] .
Resilience also plays a mitigating role in suicidal ideation among individuals with depression and anxiety. Research indicates that bolstering resilience can help moderate the risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors, underlining its critical role in mental health interventions [1] .
Resilience in Practice: How to Build and Strengthen This Vital Skill
Developing resilience is an ongoing process that involves cultivating specific mental, emotional, and social skills. According to Mayo Clinic, resilience enables individuals to harness inner strength, adapt to hardship, and rebound from setbacks in all areas of life [4] . Here are actionable steps to begin strengthening resilience:

Photo by Jonny Gios on Unsplash
- Foster Healthy Connections: Build and maintain supportive relationships with family, friends, or professionals. Reaching out for help is a key component of resilience, countering the misconception that resilience means going it alone [4] .
- Develop Problem-Solving Skills: Approaching challenges with a sense of control and adaptability allows you to break down obstacles and respond thoughtfully rather than react impulsively. Practicing mindfulness and deliberate coping strategies can be transformative [5] .
- Maintain a Positive Outlook: Cultivate optimism and gratitude by reflecting on strengths, achievements, and sources of meaning. Techniques such as journaling and reframing negative thoughts can encourage growth from adversity and promote mental well-being [2] .
- Take Care of Physical Health: Regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and adequate sleep contribute to emotional stability and resilience, supporting the mind-body connection critical to recovery [2] .
- Seek Professional Support: If you struggle with chronic stress, anxiety, or depression, consider consulting a licensed mental health professional. Therapy, counseling, or resilience training programs can provide tailored strategies and ongoing support [4] . In crisis situations, such as suicidal thoughts, immediately contact the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline or call 911.
Real-World Examples: Resilience in Action
During the COVID-19 pandemic, many individuals faced unprecedented loss, isolation, and uncertainty. Some experienced flourishing mental health despite adversity, attributed to adaptive coping mechanisms and resilient mindsets. For example, individuals who maintained social connections through virtual platforms, established routines, and practiced mindfulness reported greater emotional stability and faster psychological recovery [5] .
Workplaces and schools increasingly recognize the importance of resilience training to support well-being. Programs that teach stress management, emotional regulation, and communication skills have been shown to reduce absenteeism, improve productivity, and foster positive cultures [4] .
Potential Challenges and Solutions in Building Resilience
While resilience can be strengthened, certain barriers may impede progress for some individuals. Chronic stress, unresolved trauma, or limited access to social support can make adaptation difficult. It is important to approach resilience-building with patience and flexibility:
- Challenge: Feeling isolated or unsupported. Solution: Reach out to community organizations, support groups, or mental health professionals. Many services are available online or through local healthcare providers. Search for “mental health support” along with your city or region to find accessible resources.
- Challenge: Persistent negative thinking or hopelessness. Solution: Practice cognitive-behavioral strategies such as reframing, mindfulness, and gratitude exercises. Professional counseling can provide additional tools.
- Challenge: Difficulty maintaining healthy routines during stress. Solution: Set small, achievable goals and celebrate incremental progress. Use reminders, schedules, or accountability partners to support consistency.
Alternative Approaches for Enhancing Resilience
Different individuals may benefit from unique approaches to resilience-building. In addition to traditional psychotherapy, alternative methods such as group workshops, peer mentoring, and self-help resources can foster resilience. Consider exploring:
- Online resilience training programs offered by healthcare organizations or universities.
- Community centers and non-profits that provide stress management workshops and support groups.
- Books, podcasts, or webinars by reputable psychologists and mental health experts.
To find programs, use search terms like “resilience training” or “stress management workshop” with your location.
How to Access Resilience Resources and Support
Resilience-building services may be available through your healthcare provider, workplace wellness program, or local mental health agency. For tailored support:
- Contact your primary care physician for referrals to licensed therapists or counselors specializing in resilience training.
- Check with your employer about employee assistance programs (EAPs) that offer mental health resources.
- Search for community mental health centers or non-profit organizations providing resilience workshops and support groups.
- In urgent situations, reach out to crisis hotlines such as the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline or call 911 for immediate support.
It’s always recommended to seek guidance from recognized organizations and professionals. Avoid websites or programs that lack verified credentials or reviews.
Key Takeaways
Resilience is a vital foundation for mental well-being. By developing adaptive coping skills, nurturing supportive relationships, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, individuals can protect themselves against depression, anxiety, and the harmful effects of chronic stress. There are numerous pathways to build resilience, from professional therapy to community workshops and self-guided learning. Remember, everyone’s journey is unique, and support is available. If you face challenges in building resilience, consult healthcare professionals and reputable organizations for personalized assistance.
References
- [1] Southwick et al. (2016). Resilience: A psychobiological construct for psychiatric disorders.
- [2] Harvard Health (2022). Ramp up your resilience!
- [3] Srivastava et al. (2012). Positive mental health and its relationship with resilience.
- [4] Mayo Clinic (2023). Resilience: Build skills to endure hardship.
- [5] El Camino Health (2022). Resilience and Your Mental Health.
MORE FROM eboxgo.com